How Certain Plants Trigger Human Cell Regeneration: Lessons from Nature
This article explores the fascinating realm of plant-derived compounds and their potential to stimulate human cell regeneration. We’ll examine specific plants known for their regenerative properties, uncover the mechanisms by which they influence cellular processes, and discuss practical ways these natural compounds can support tissue repair. Importantly, we’ll focus on lifestyle-accessible remedies, making the science of regeneration approachable for everyday use.
Introduction to Plant-Based Regeneration
The human body has an incredible capacity for self-repair, yet this ability declines with age and can be insufficient in the face of injuries or chronic disease. Regenerative medicine aims to restore or enhance damaged tissues, and plants provide a rich source of bioactive compounds that may stimulate this process.
Interestingly, many plants have evolved to heal themselves after injury. The compounds responsible for these regenerative abilities—like flavonoids, polysaccharides, and terpenoids—can influence human cells by promoting cell growth, differentiation, and survival.
Key Plants and Their Regenerative Properties
1. Aloe Vera
Primary compounds: Polysaccharides, enzymes, antioxidants
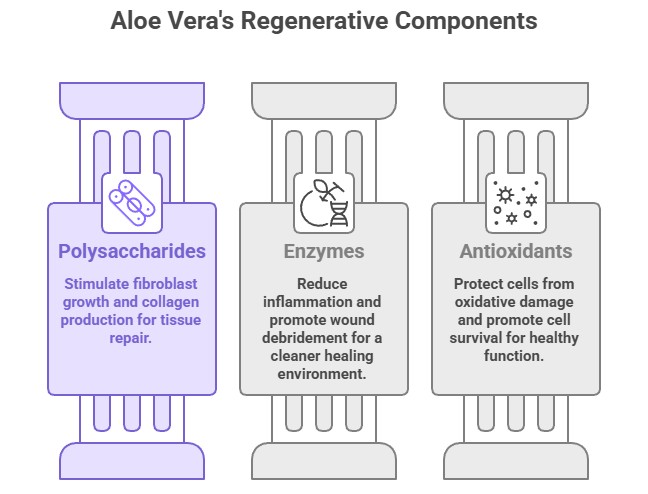
Aloe vera is a succulent renowned for its ability to promote wound healing and tissue repair. Its gel contains compounds that stimulate fibroblast proliferation, increase collagen synthesis, and accelerate new blood vessel formation—all essential for regeneration.
Mechanism of Action:
- Polysaccharides: Stimulate fibroblast growth and collagen production
- Enzymes: Reduce inflammation and aid wound debridement
- Antioxidants: Protect cells from oxidative damage and enhance cell survival
Lifestyle tip: Apply fresh aloe gel to minor cuts or burns. Aloe juice can also support digestive health internally.
2. Centella Asiatica (Gotu Kola)Primary compounds: Asiaticoside, madecassoside, asiatic acid
Known for its wound-healing and skin-regenerating properties, Gotu Kola stimulates collagen synthesis, improves blood circulation, and reduces inflammation.
Mechanism of Action:
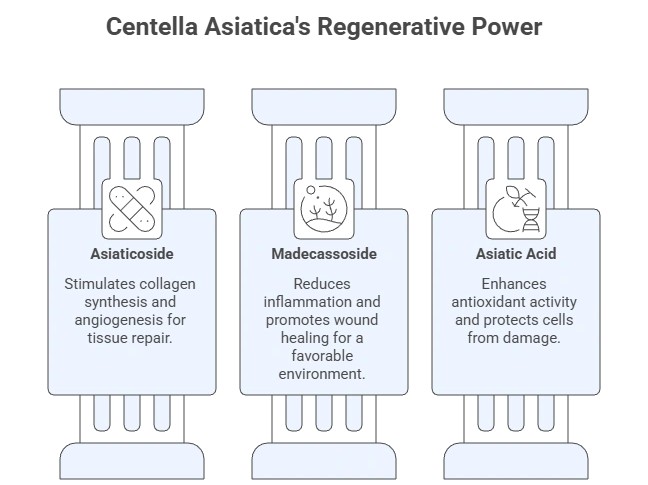
- Asiaticoside: Promotes collagen production and angiogenesis
- Madecassoside: Reduces inflammation and supports tissue repair
- Asiatic Acid: Enhances antioxidant activity and protects cells
Lifestyle tip: Use Gotu Kola leaf extracts in teas, smoothies, or topical creams for skin health.
3. Calendula Officinalis (Marigold)
Primary compounds: Triterpenoids, flavonoids, carotenoids
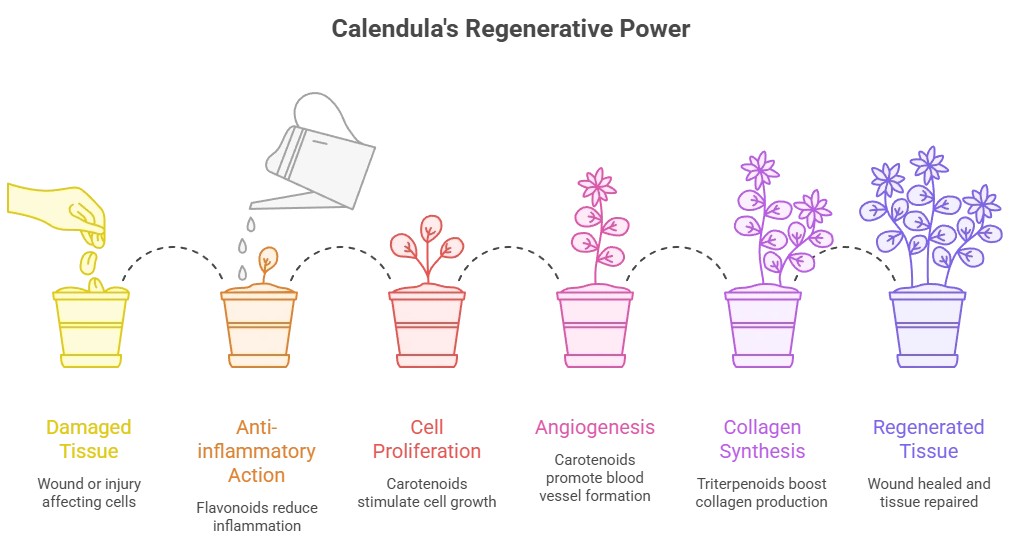
Calendula accelerates wound closure by stimulating cell proliferation, collagen synthesis, and angiogenesis. Its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties make it a popular choice in skincare.
Mechanism of Action:
- Triterpenoids: Boost collagen synthesis and wound contraction
- Flavonoids: Reduce inflammation and oxidative stress
- Carotenoids: Promote cell proliferation and blood vessel formation
Lifestyle tip: Calendula-infused oils or creams can be applied to minor skin irritations and wounds.
4. Symphytum Officinale (Comfrey)
Primary compounds: Allantoin
Comfrey is historically used for wound and bone healing. Allantoin stimulates new cell growth and accelerates tissue regeneration. Due to potential liver toxicity from pyrrolizidine alkaloids, topical application is preferred over ingestion.
Mechanism of Action:
- Allantoin: Encourages cell proliferation and tissue repair
5. Equisetum Arvense (Horsetail)
Primary compounds: Silica, antioxidants
Horsetail supports collagen synthesis and bone formation thanks to its high silica content. Antioxidants further protect cells and promote tissue survival.
Mechanism of Action:
- Silica: Strengthens connective tissue and bones
- Antioxidants: Mitigate oxidative stress and protect regenerating cells
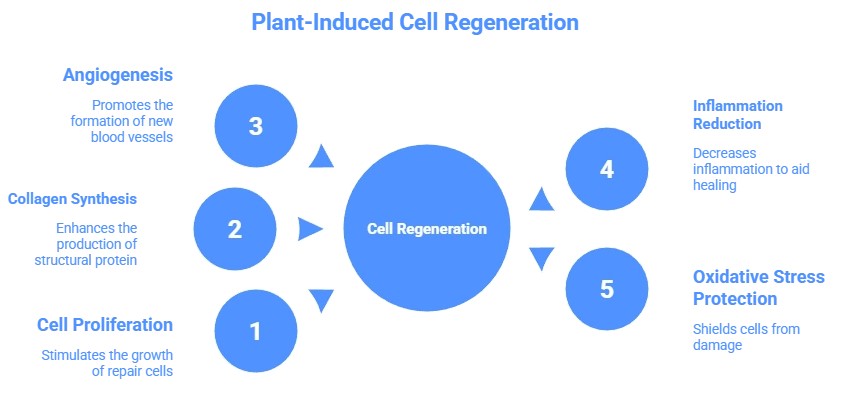
Mechanisms of Plant-Induced Cell Regeneration
Plant compounds stimulate human cell regeneration through several interconnected processes:
- Stimulation of Cell Proliferation: Compounds in plants can activate fibroblasts, keratinocytes, and endothelial cells, key players in tissue repair.
- Enhancement of Collagen Synthesis: Collagen is crucial for connective tissue and skin regeneration; plant bioactives boost its production.
- Promotion of Angiogenesis: Formation of new blood vessels ensures oxygen and nutrients reach regenerating tissues.
- Reduction of Inflammation: Anti-inflammatory plant compounds help prevent tissue damage and support healing.
- Protection Against Oxidative Stress: Antioxidants from plants protect regenerating cells from free radical damage.
Implications for Regenerative Medicine
The regenerative potential of plants extends beyond the kitchen or garden and holds promise for therapeutic applications:
- Wound Healing: Plant-based creams can accelerate closure and tissue repair in burns, ulcers, or surgical wounds.
- Skin Regeneration: Skincare products containing plant extracts can improve elasticity, reduce wrinkles, and stimulate repair.
- Bone Regeneration: Silica-rich and collagen-promoting plants may accelerate fracture healing.
- Organ Regeneration: Research is ongoing to explore plant compounds in supporting organ repair in cases of organ failure.
Challenges and Future Directions
While promising, plant-based regenerative therapies face some challenges:
- Standardization: Active compounds vary by plant source, harvesting methods, and extraction techniques.
- Identification of Key Molecules: Understanding which compounds drive regeneration is essential for targeted therapies.
- Mechanistic Research: Further studies are needed to unravel the cellular pathways affected by plant bioactives.
- Clinical Trials: Rigorous trials are necessary to confirm safety and efficacy in humans.
Future research should focus on translating traditional knowledge and preliminary studies into evidence-based therapies.
Conclusion
Plants offer remarkable regenerative properties, providing bioactive compounds that stimulate human cell repair, collagen synthesis, angiogenesis, and anti-inflammatory pathways. By integrating these lifestyle-accessible remedies—such as aloe vera, Gotu Kola, calendula, comfrey, and horsetail—into daily routines, we can harness nature’s regenerative wisdom.
While challenges remain in standardization and clinical validation, the potential of plant-based regeneration is immense, offering a natural complement to modern regenerative medicine and therapies.

